How to Write B2B Emails
Introduction
Email communication plays a pivotal role in the success of B2B companies. Unlike consumer audiences, professional buyers demand relevant, tailored, and valuable information. These will guide their logical decision-making process. B2B marketers who can cut through the noise and deliver targeted email campaigns at each stage of the sales funnel reap huge rewards. Studies show that email drives around 20% of revenue for B2B firms by:
- Generating new prospects
- Nurturing existing opportunities
- Driving conversions
However, sending high volumes of emails is not enough. You need to craft compelling messages that spark engagement and build relationships. This comprehensive guide will explore the art of writing stellar B2B emails. It will outline actionable tips and strategies. This piece will help you deliver the right content to the right prospects at the right time. It will aid you if you’re looking to master email outreach for lead generation. You can also use it to improve campaign relevance for your existing customer base.
Follow this structured playbook to capture attention, convey value, and boost email metrics. Improve your open, click-through, and conversion rates. With the tools and templates provided, you will be able to create consistent yet tailored emails. They will move prospects down the sales funnel.
Understanding B2B Emails
B2B emails differ greatly from business-to-consumer (B2C) emails in the following:
- Fundamental goals
- Target audience
- Call-to-action
B2C emails targeting retail consumers often aim to drive quick sales or build brand awareness. They accomplish this through campaigns like promotions, newsletters, and surveys. Engagement is measured by metrics like open and click-through rates.
However, the audience for B2B emails comprises professional buyers. They’re typically in roles like managers, directors, vice presidents, and C-level executives. Rather than targeting individuals, your emails speak to an organization’s worth of stakeholders. Each one is represented by the recipient. These buyers make logical, calculated decisions about products and services for their company. They don’t make emotions-based personal purchases. As such, B2B emails play a key role in driving conversions within a longer, complex B2B sales cycle by:
- Generating new leads in the early awareness phase, which later turns into a sales-qualified pipeline. This requires casting a wide net with relevant messaging to identify prospects by role, industry, company size, and tech stack.
- Nurturing opportunities through the middle stages. Provide ongoing value and building relationships with decision-makers and budget authorities. Content like case studies, analyst reports, and product guides aids consideration.
- Accelerating deal closure once hands-on evaluations start by coordinating demos, trials, and paperwork. Hyper-targeted communication minimizes delays.
- Expanding existing customer accounts through renewal, upsell, and cross-sell. Understanding usage data helps craft appropriate offers.
B2B buyers are demanding much more information across channels through the purchasing process. Email remains the digital backbone for marketers to nurture every account from awareness to advocacy. But this needs knowing your audience segments to deliver tailored value across the customer lifecycle.
The Anatomy of an Effective B2B Email
This breaks down the key ingredients that comprise compelling B2B emails. It analyzes the critical components that influence engagement and response rates.
Subject line
The Subject Line makes that vital first impression within the inbox. It needs attention-grabbing tactics to spark open rates while avoiding spam filters. Employing specificity and personalization here drives higher open rates. Analyze the subject line length, power words used, branding presence, and results from A/B testing various options.
Opening line
The Opening Line determines whether your message will be skimmed or skipped upon opening. Make an emotional connection or highlight a shared frustration right up front before conveying value. This will set the tone that resonates with readers. Short opening lines or questions that establish relevance seem to work best for reader retention.
Body Content
The Body Content must communicate tangible business value centered around the following:
- Understanding needs
- Solving problems
- Improving outcomes
- Addressing organizational goals
This requires having an intimate understanding of your prospect’s role, pain points, and objectives. Section headers, tightly written paragraphs, testimonials, and ample white space improve immobility. It enhances the retention of key messaging for busy executives.
Call-To-Action
Finally, the Call-To-Action must provide clear next steps for the prospect upon consuming the content. It may be scheduling a meeting, registering for a demo, attending a webinar, or continuing the conversation. The CTA should stand out visually and use urgent language to compel the desired outcome. Experiment with CTA placement, format, content, and visual treatment to drive higher response rates.

Step-by-Step Guide to Writing B2B Emails
Step 1: Identify Your Objective
It can be generating leads, nurturing existing opportunities, driving conversions, or expanding accounts. Define success metrics upfront tied to pipeline growth, deal velocity, or customer lifetime value. For example, you may aim to achieve a 25% open rate and 5% click-through rate for a lead nurture campaign targeting the directors at 500 mid-sized law firms. Or your goal could be booking 10 discovery calls from a 100-touch outbound cadence. Having quantifiable goals guides better email design and messaging.
Step 2: Know Your Audience
Thoroughly research prospect demographics like seniority, role, title, industry, and company size. This enables personalization with contextual relevance. Additionally, analyze historical campaign data. It reveals which messaging angles and content types resonate with each target segment you plan to pursue. For instance, financial services prospects may be more receptive to credibility drivers. Examples include analyst reports, security white papers, and prestigious client logos. Meanwhile, creative agencies prefer more visual presentations.
Step 3: Craft Compelling Subject Lines
Use tailored hooks or urgent headers aligned to their business priorities. You can utilize thought-provoking questions that break through the noise. Subject lines under 50 characters driving specificity have much higher open rates in crowded inboxes. So avoid being generic. Additionally, continuously A/B tests different subject line options and keywords. This empirically optimizes performance over successive campaigns.
Step 4: Write Engaging Content
It should be centered around the prospect’s pain points and business objectives. Establish quick relevance to their role right up front rather than starting with a product pitch. Use scannable formatting with short tight paragraphs. Focus on outcomes, statistics, vision, and success stories from similar companies rather than blocks of dense text. Convey deep expertise through well-articulated points of view.
Step 5: Tailor Your Copy
Incorporate contextual details about the prospect’s background. This reinforces why it specifically matters to them. The best emails feel like one-to-one conversations even when sent at scale, rather than mass blasts. This is achievable through diligent research. Combine it with merge tags in the subject line and content body to populate individual specifics. Personalized emails have about a 30% higher open rate on average.
Step 6: Prominently Include Strong Calls-to-Action
Provide clear next steps. Examples of this include the following:
- Downloading an educational asset
- Scheduling a meeting
- Registering for an event
- Continuing the nurture dialogue
Compelling CTAs with aesthetically contrasting design and urgent language stand out better. They also drive more clicks. Additionally, place primary and secondary CTAs strategically in emails. This is based on established eye-tracking scan patterns.
Step 7: Conclude with a Warm, Professional Closing
It should positively yet briefly summarize the important elements of your core proposition. At the same time, it seals your brand presence as a trusted advisor. Always close by offering convenient contact details and hyperlinks. These empower recipients to follow up or learn more on their own schedule after reading. This drives further engagement.

7 Exceptional B2B Email Templates
- The New Customer Welcome Email

Source: Lyft
Make new users feel valued while orienting them to get started with your product or service. Use onboarding checklists and dedicated support channels.
- The Targeted Campaign Promotion
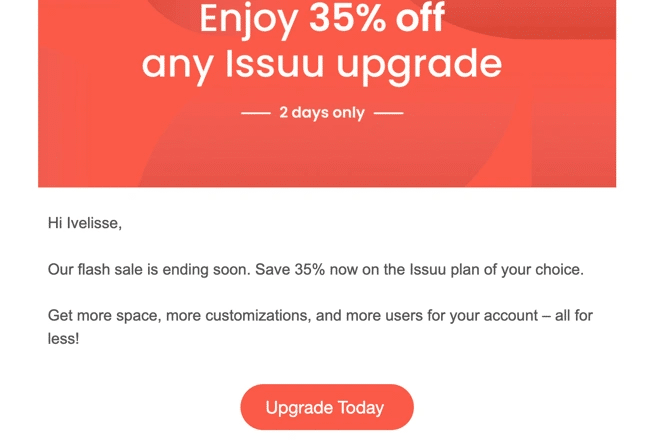
Source: Issuu
Create urgency and exclusivity for time-bound offers to high-value segments. This is identified by their role, industry, behavior, or milestone trigger.
- The Customer Retention Playbook
Source: Autotrader
Build loyalty through special guides, worksheets, or templates. Helping customers continually gets more value from your solution.
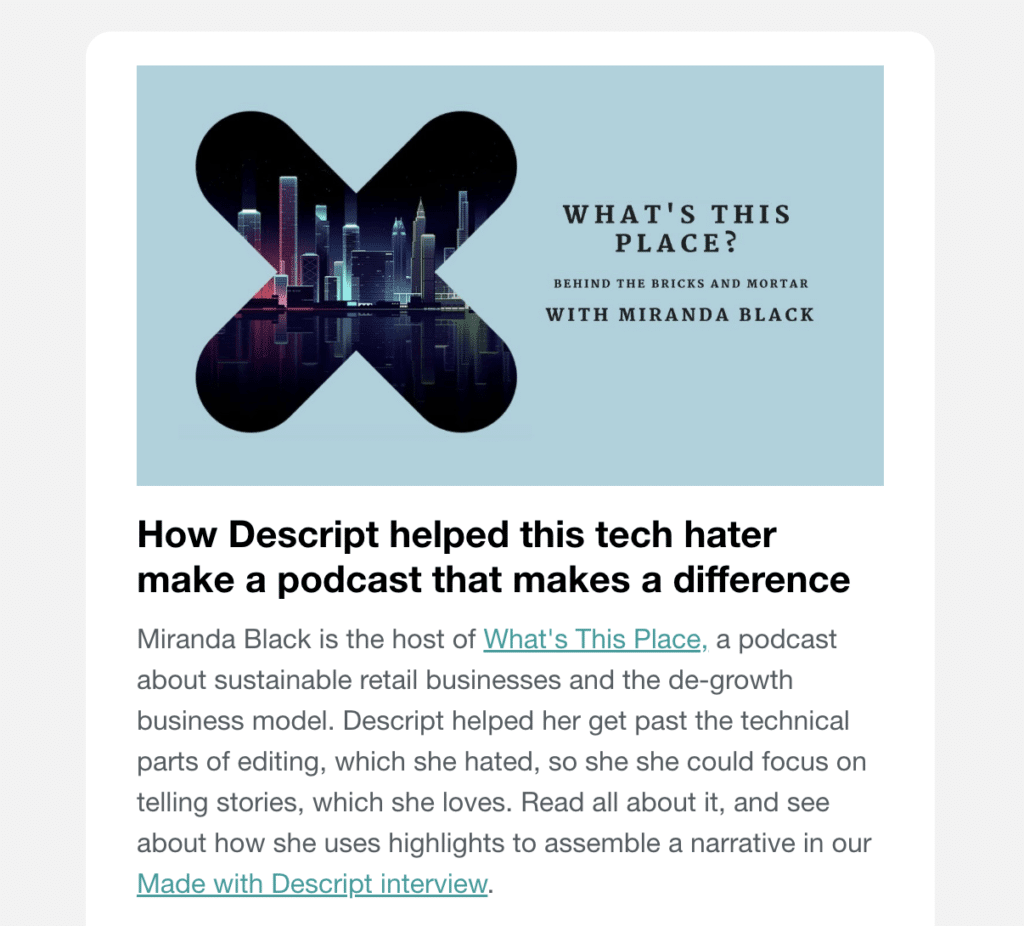
- The Case Study Email
Source: Descript
Highlight a customer success story focused on ROI and metrics they care about. Use a structured narrative documenting the transformation.
- The Negatives Into Positives Email
Source: HubSpot
Address common customer issues, questions, or objections. Include content pre-empting and overcoming them through education.
- The Direct Book Meeting Outreach
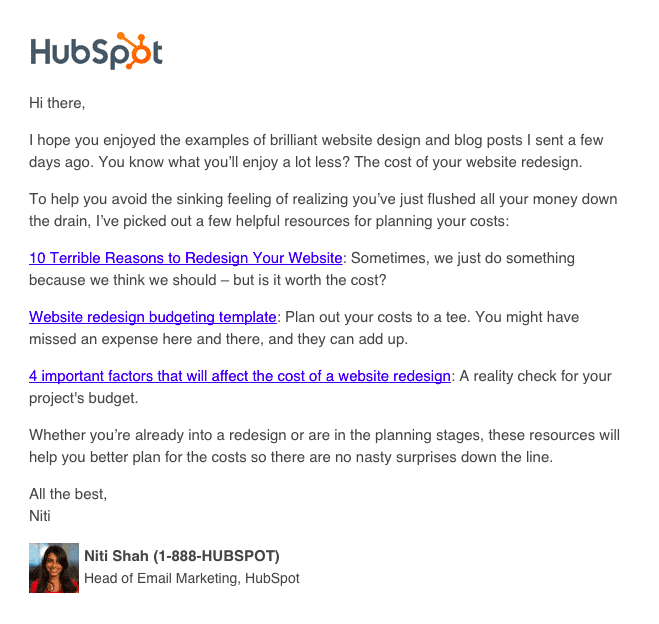
Source: Doctor On Demand
Make meetings easy to schedule for busy executives. Link calendar integration, propose agendas, and state value.
- The Event/Webinar Promotion

Source: SimilarWeb
Create exclusive events to bring together peer groups and position thought leadership. Use compelling subject lines and built-in urgency.
Each template can be adapted to specific customer segments as outlined earlier. Follow the core framework while customizing examples, stats, offers, and more.
Advanced Tips and Strategies
Effective email copywriting should use research-backed psychological triggers that motivate action. For example, reciprocation triggers make audiences feel obligated to respond to the value provided for free. Meanwhile, scarcity urgency compels taking advantage of limited-time exclusives. Similarly, social proof through peer stats and testimonials reinforces decisions.
Storytelling also better conveys complex services by documenting a structured narrative arc. It should be focused on transformation. For example, case studies chronicle the sequence of the following:
- Defining a problem
- Strategizing the approach
- Executing initiatives
- Quantifying ROI
This resonance and retention carry email messaging beyond a sales pitch.
Advanced personalization powered by predictive intelligence also boosts relevancy. Send times can be customized based on each recipient’s typical reading periods. Dynamic content draws from individual activity to address specific pain points. Personalized subject lines have open rates up to 50% higher than a generic copy.
Audience segmentation is crucial for grouping contacts to run targeted campaigns. The most common dimensions to filter by include industry, title/role, company size, geography, and lead stage. However, behavioral segmentation based on engagement levels takes relevancy a level deeper.
Testing and optimization should fuel continual email program improvement. A/B testing subject lines is simple using dedicated tools. The best-performing components can then be combined into new templates optimized for key metrics like open rates. Analyze performance data down to the reader level. It identifies both high-potential targets and disengaged contacts for more aggressive re-targeting.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
There are a few common mistakes made in B2B emails that marketers should be aware of:
- Sending overly promotional messages rather than value-driven content will turn off prospects. Provide educational assets focused on addressing business needs rather than constant product pitches.
- Failing to research and segment your distribution lists leads to irrelevant messaging. You miss the mark for specific contacts based on their role, industry, or company. Tailor content accordingly.
- Using boring generic subject lines and greetings rather than tailored hooks causes emails to be ignored. Include specific details to stand out.
- Writing dense text-heavy emails that are difficult to scan discourages engagement. This is especially true for busy executives seeking rapid value. Improve immobility through tight paragraphs, ample white space, and clear formatting.
- Neglecting to include a solid CTA leaves readers without clear direction on the desired next steps. They won’t know how to continue the conversation. Compel specific click-throughs.
With mindful planning tailored to recipients and continual optimization, these pitfalls are avoidable. You can maximize email effectiveness.
Measuring Success: B2B Email Metrics
Several metrics that show how an email campaign has achieved its objectives:
- Open Rates
They reveal how attention-grabbing your subject lines and sender information appear. Industry averages range from 10-25%.
- Click-through rates
They show content relevance by measuring navigation to links and assets embedded in emails. For B2B, 2-5% is typical.
- Conversion Rates
They show how effectively your call-to-actions drive the desired prospect behavior. It ranges from content downloads to form fills to purchases. These vary significantly by industry and campaign goals but should be defined and tracked.
- Unsubscribe Rates
They help gauge overall reader satisfaction and engagement with your ongoing communications. These should stabilize below 0.5% otherwise messaging may need to be refined.
Besides primary metrics, view-to-open ratios assess preview pane usage. At the same time, buyer response times show urgency. Analyze metrics trends across segments and campaigns to continuously optimize.
Adapting to Industry and Cultural Variations
Best practices exist for structuring professional emails. However, execution should adapt across unique B2B environments. Conservative fields like finance or healthcare warrant more formal conservative tones avoiding colloquialisms. Meanwhile, creative industries permit personalized expression. Regional cultural differences also matter. Eastern cultures prefer formal hierarchies while Western communication is more direct.
Additionally, specialized vocabularies and frustrations inherent to each industry should guide relevant messaging. For example, manufacturing prospects care about supply chain barriers. Retail is concerned with client loyalty tactics. Software companies focus on scalability. Localize subject lines, statistics, and imagery accordingly.
With tailoring to industry norms and regional sensitivities, global B2B email initiatives can resonate across key markets.
| Industry | Communication Style | Specialized Vocabulary | Localization Needs |
| Finance/
Healthcare |
Formal, conservative, avoid colloquialisms | Compliance, risk management, patient privacy, financial stability | Use formal titles, respect hierarchical structures, use industry-specific data |
| Creative Industries | Informal, personalized, open to creative expression | Innovation, design trends, audience engagement | Use more vibrant imagery, casual language, highlight creativity |
| Manufacturing | Professional, focused on efficiency and reliability | Supply chain logistics, production efficiency, quality control | Highlight local manufacturing capabilities, industry-specific regulations |
| Retail | Engaging, customer-centric, often informal | Customer loyalty, sales trends, product placement | Use local consumer behavior, seasonal trends, and success stories |
| Software/
Technology |
Informative, can be technical, focus on innovation and scalability | Software scalability, data security, user experience | Reference local tech advancements, regulatory considerations |
| Eastern Cultures | Formal, respectful, hierarchical | Industry-specific but with a focus on respect and formality | Use respectful language, understand local business practices |
| Western Cultures | Direct, straightforward, less hierarchical | Industry-specific but generally more direct and problem-solving focused | Use a more direct approach, be clear and concise |
Legal and Ethical Considerations
When managing email distribution lists, marketers must follow country and region-specific regulations. These revolve around commercial messaging consent. For example, GDPR policies need clear opt-in and unsubscribe mechanisms for EU contacts. CAN-SPAM provides guidelines for the US while CASL governs Canada. Stay up to date on policies.
Ethically, the following builds trusted relationships with subscribers and protects the sender’s reputation:
- Transparency around mailing list sources
- Providing unsubscribe access
- Avoiding misleading language
Maintain strict data security as well. Follow best practices surrounding confidentiality, integrity, and availability of contact information.
Leveraging Technology: Tools and Automation
Sophisticated tools and software platforms streamline executing scalable, high-performing, and compliant email campaigns:
- CRM/MAP systems like Salesforce, HubSpot, and Marketo manage subscriber data. They integrate with workflows, track interactions and dynamically populate campaign templates for personalization.
- Email service providers like MailChimp, Constant Contact, and GetResponse enable designing templates. They allow you to send bulk messages and track performance.
- Predictive intelligence features score leads, trigger tailored content, and optimize send times. It’s to improve open rates.
Together, these solutions drive automation across subscribers, templates, and analytics. They allow marketers to focus on strategy rather than repetitive tasks. This optimization allows continually testing content variations to improve results.
Conclusion
Email marketing remains an indispensable channel. It engages professional buying teams during every B2B customer lifecycle stage. But effectively cutting through noise requires an orchestrated approach to genuinely convey value. Focus on delivering relevance over promotions through research, segmentation, and personalization. It should be tailored to the role and industry.
Craft compelling subject lines, opening hooks, and scannable content. Focus on addressing frustrations then compel action via prominent CTAs. Study critical email metrics diligently to fuel ongoing optimization toward key performance indicators. With continuing refinement guided by data, B2B marketers can maximize email ROI. At the same time, build durable customer relationships through consistently professional communication.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I send B2B emails to avoid being labeled as spam?
A good rule of thumb is to avoid sending marketing emails to the same audience more than once or twice per week. Over-communication can feel intrusive and have diminishing returns. Send quarterly or monthly nurture emails along with more urgent promotional bursts. It can positively engage audiences. Also, ensure you provide easy subscription management and an unsubscribe link.
What are the optimal list sizes for effective B2B email campaigns?
B2B email lists should balance quality over quantity to optimize relevance. Typical best-practice sizes range from 50,000 to 500,00. The former is for new businesses promoting their brand. The latter is for established companies nurturing longer complex sales cycles. Rather than amassing every possible contact, focus on high-intent segments. They should align with buyer personas through lead scoring.
How does writing style impact B2B email performance?
Executives prefer clear, commanding yet conversational language from subject lines to content. Avoid overly formal bureaucratic jargon or overly casual character limits seen in social posts. Relatable writing helps emails resonate like one-on-one talks. An expert yet approachable voice builds connections over time.
When during the workweek should important B2B emails be deployed?
Sending early on Tuesday, Wednesday, or Thursday mornings has proven best for engagement. Executives plan priorities midweek. Mondays bring hectic catchups from weekends while Fridays tend to wrap up outgoing tasks before the next week. Scheduling email delivery when audiences are most receptive maximizes impact.
What tools can help my small business write better B2B emails?
Many email marketing platforms offer DIY design templates to maintain brand consistency. They also offer tools to A/B test subject lines plus preview content across devices. Small teams can also leverage AI copywriting assistants to optimize messaging. Focus resources on strategy and execution over starting from scratch.